
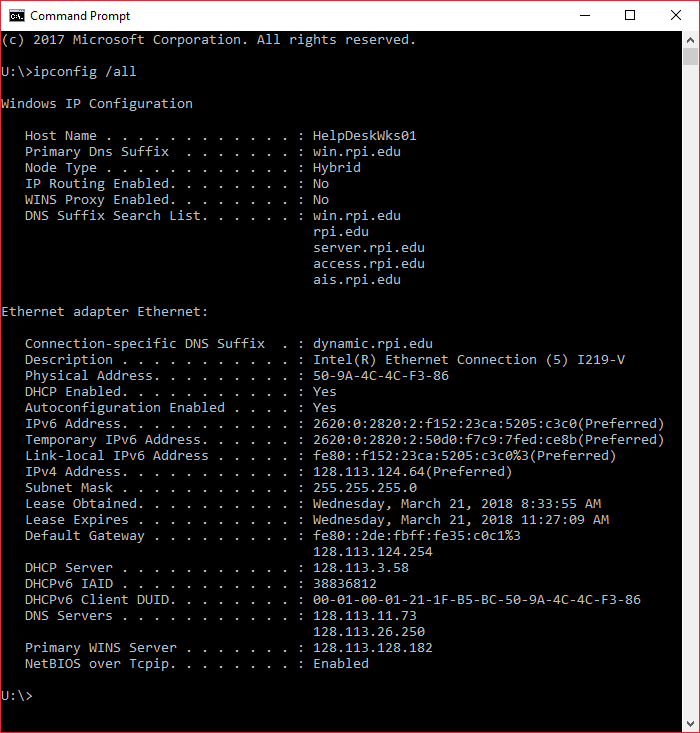
TX packets:4198 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 RX packets:4198 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 The output includes information about all active and inactive network interfaces: docker0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 56:84:7a:fe:97:99 When invoked without any options, ifconfig displays the configuration information of all network interfaces and associated ip address: ifconfig -a Display Information of Network Interfaces # Only root or users with sudo privileges can configure network interfaces. To make the changes permanent, you need to edit the distro-specific configuration files or add the commands to a startup script. After a system restart, all changes are lost. The configurations set with the ifconfig command are not persistent. address - is the IP address that you want to assign.interface - is the name of the network interface.The basic syntax of the ifconfig command is shown below:
To install ifconfig on CentOS and other RHEL based Linux distros, type: sudo dnf install net-tools -y How to Use the ifconfig Command # On Ubuntu and Debian-based based Linux distributions, run the following command to install ifconfig: sudo apt install net-tools -y Install ifconfig on Centos # If you get an error message saying “ifconfig: command not found”, it means that the package that contains the command is not installed on your system. The ifconfig command is deprecated and replaced with ipĪnd may not be included in the newer Linux distributions. In this article, we’ll explore how to use the ifconfig command. With ifconfig, you can assign IP addresses, enable or disable interfaces, manage ARP cache, routes, and more.
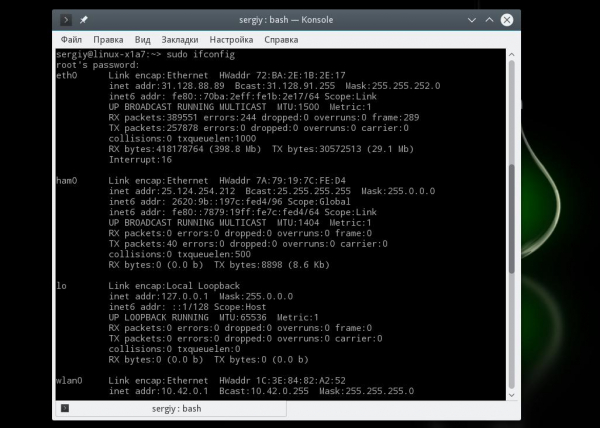
It is used to configure and view the status of the network interfaces in Linux operating systems. Ifconfig (interface configuration) is a network management tool.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
